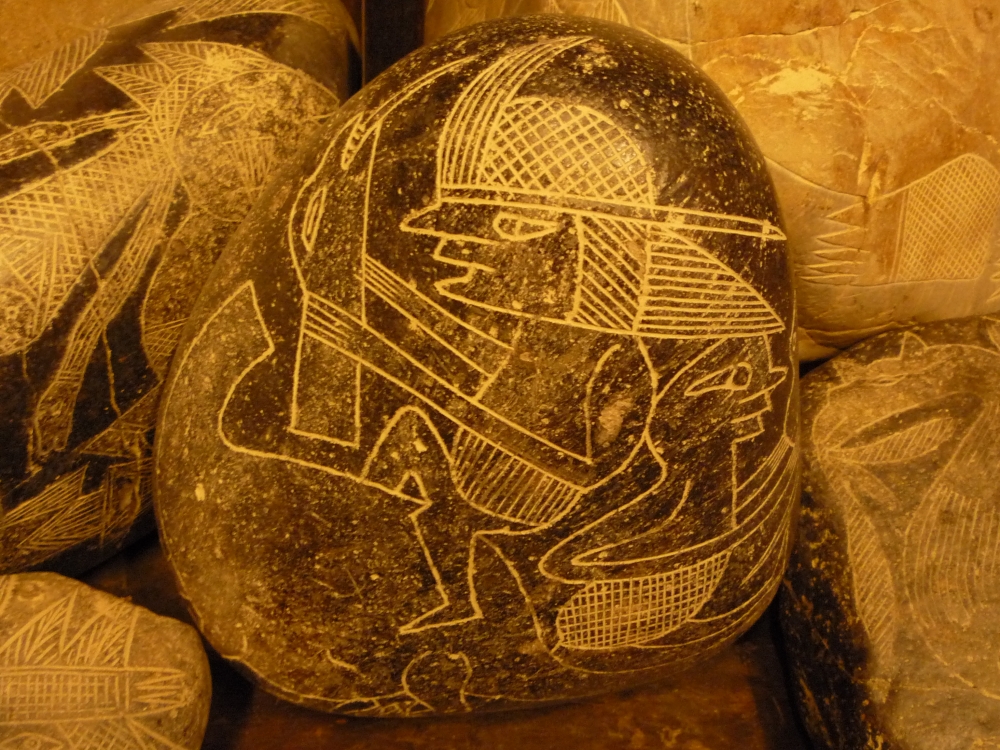
The ancient civilization of Babylon, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, has left an indelible mark on history. Among the remnants of this once-great empire, the sacred boundary stones, or kudurrus, stand as silent sentinels, bearing witness to the rich cultural tapestry and religious beliefs that defined Babylon.
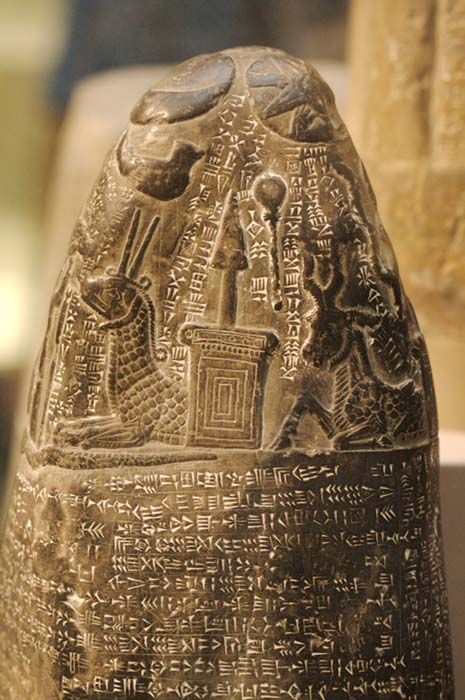

In this exploration, we unravel the significance of these boundary stones and the unique signs that distinguish Babylon as a civilization unlike any other. The fertile lands between the Tigris and Euphrates nurtured Babylon as a prominent civilization in ancient Mesopotamia.
The kudurrus, sacred boundary stones of Babylon, held immense religious and legal importance, marked by unique inscriptions, symbols, and depictions. Babylon’s religious practices, characterized by syncretism and polytheism, are reflected in the worship of a pantheon of deities, as depicted in the sacred inscriptions on the kudurrus.
Babylon’s cultural and artistic achievements flourished, with intricate carvings and artistic expressions showcased on the kudurrus. These stones, beyond demarcating sacred boundaries, served as legal documents detailing land grants, agreements, and social hierarchies.
Babylonian cosmology, influenced by celestial observations and astrological significance, is evident in the symbolism of the kudurrus. Technological advancements and architectural marvels in Babylon influenced the construction and inscriptions on the kudurrus, reflecting pride in engineering prowess and cultural identity.