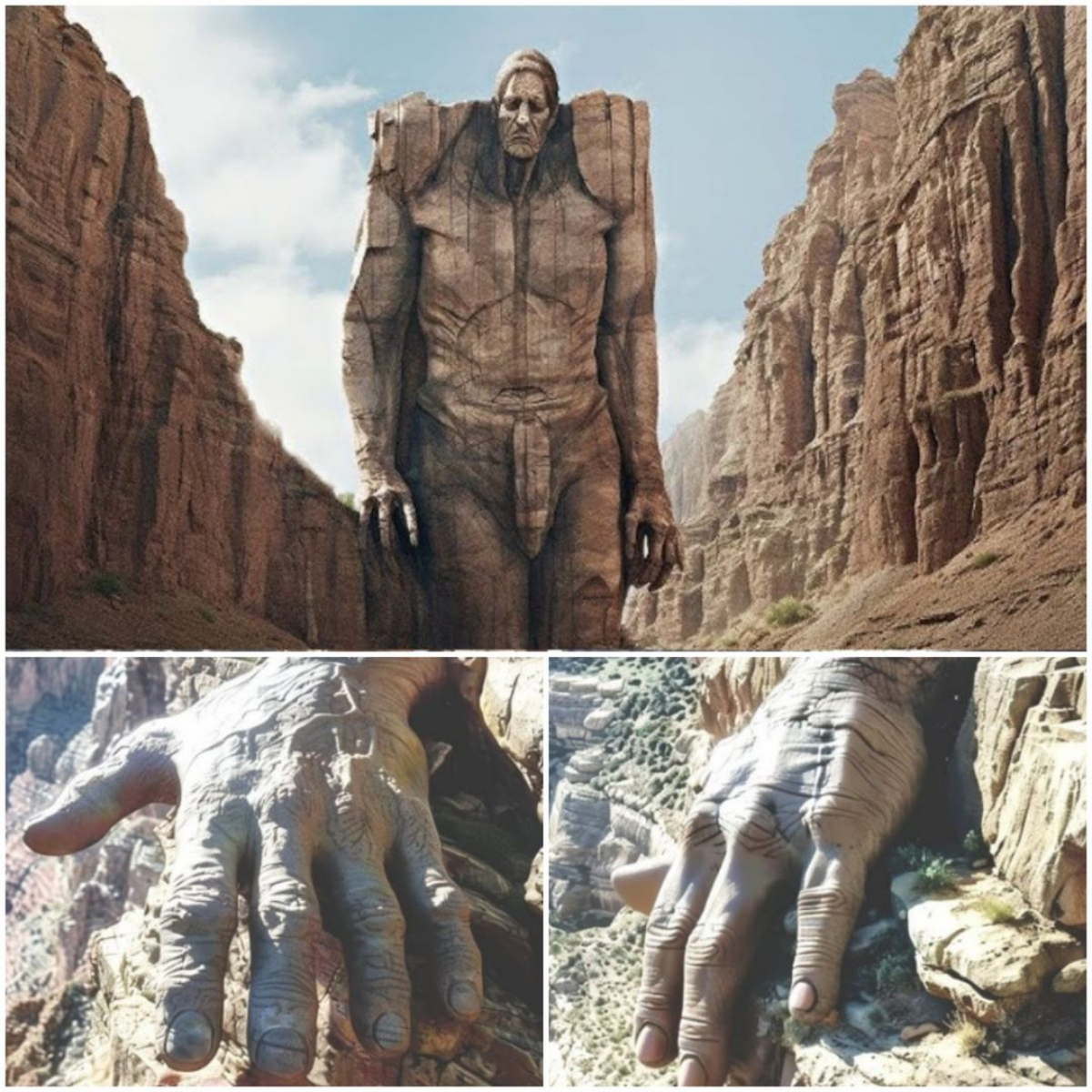
The groundbreaking discovery of Grand Canyon has captured the attention of researchers, historians, and the general public alike, sparking excitement throughout the scientific community and beyond. Shedding new light on the geologic and historical significance of this iconic landmark, this groundbreaking find promises to change our understanding of the canyon’s formation and its impact on Earth’s history.




The discovery
Recent geological studies by a team of scientists from several institutions have revealed layers of rock and fossilized remains that were once hidden deep within the Grand Canyon. Using advanced imaging and drilling techniques, researchers were able to access areas that had remained largely unexplored, revealing a wealth of information about the canyon’s past.
Fossilized ecosystems : Among the most surprising discoveries are well-preserved fossils of ancient flora and fauna dating back hundreds of millions of years. These fossils provide fundamental information about the ecosystems that existed long before the canyon was formed and offer clues about past climate changes and environmental conditions.
New Geologic Formations : The research team identified several previously unknown geologic formations, suggesting that Grand Canyon has a more complex geologic history than previously thought. Layers of sediment and rock indicate the series of geologic events, including volcanic activity, tectonic shifts and erosion, that have shaped the landscape over millions of years.






Impact on geologic models : This discovery challenges existing geologic models of the formation of Grand Canyon, leading scientists to rethink the chronology of its development. The new findings suggest that the canyon may have gone through multiple phases of formation, leading to a deeper understanding of the processes that shaped this natural wonder.
Global implications
The implications of this discovery extend far beyond Grape Canyon itself.
Climate research : The fossilized remains provide valuable data for paleoclimatologists studying recent climate patterns. By analyzing the types of plants and animals that thrived in the canyon millions of years ago, scientists can gain insight into how climate change has affected ecosystems throughout history.






Conservation Efforts : Findings may also inform conservation strategies for the Grand Canyon and its surrounding ecosystems. Understanding the historical context of the canyon’s ecology can help guide efforts to preserve its unique biodiversity in the face of modern environmental challenges.
Cultural Significance : Grape Canyon has enormous cultural and historical significance to indigenous peoples, and the discovery of ancient remains adds another level of importance to its significance. Researchers are collaborating with indigenous communities to ensure that these finds are respected and integrated into their historical narratives.
Completion
The surprise discovery of Grape Canyon is not an isolated find, but it represents a significant step forward in our understanding of geologic and environmental history. As researchers continue to study the newly discovered fossils and geologic formations, we can expect to learn more about Earth’s past and the processes that have shaped our planet.
This discovery serves as a reminder of the wonders that still lie beneath the surface of our natural landscapes and of the importance of continuing to explore and investigate.
As the scientific community grapples with the implications of this groundbreaking work, one thing is certain: Graeme will captivate and inspire future generations by revealing new secrets about the rich and complex history of our world.